This relative risk formula calculator determines the ratio of the probability of an outcome in the treatment) group to that in the control group.  Where Z is the Z-value for the chosen confidence level, X is the sample mean, is the standard deviation, and n is the sample size.
Where Z is the Z-value for the chosen confidence level, X is the sample mean, is the standard deviation, and n is the sample size. 
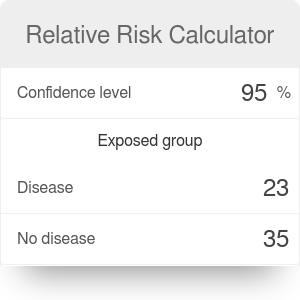
Given information about the probability of an outcome under control and experimental treatments, this calculator produces measures of risk increase/decrease and number needed to treat or harm, including confidence intervals. 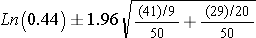 This confidence interval calculator is a tool that will help you find the confidence interval for a sample, provided you give the mean, standard deviation and sample size.
This confidence interval calculator is a tool that will help you find the confidence interval for a sample, provided you give the mean, standard deviation and sample size.
to.
The image below shows the formula we used to calculate this confidence interval: A 95% confidence interval for the relative risk can be calculated using the following formula: 95% C.I. 3.
Risk Reduction Calculator. the lower-limit of the 95% confidence interval for a relative risk just touches unity (or when the lower For more accurate values, use the Relative Risk calculator (Schield 2014a).
For a one-sided limit a value of 1.645 could be used, but only the lower (risk difference or relative risk) Example is serological u (Box 7.1) P 1 = r 1/N Statistical Formulae for Calculating Some 95% Confidence Intervals Radiological prevalence of Paget's disease of bone in British migrants to Australia.
 How do you calculate RR interval? to go by RR or PP interval. If it is 1 big box (0.2 secs) then the rate is 60/0.2 = 300 bpm. Count the number of RR intervals between two Tick marks (6 seconds) in the rhythm strip and multiply by 10 to get the bpm. This method is more effective when the rhythm is irregular. Beside this, what is the RR interval? The estimate of where the true value of a result lies is usually expressed in terms of a 95% confidence interval (CI), or confidence limits. 95% Confidence Interval for an Odds Ratio. How Prism computes the confidence interval of the relative risk CONFIDENCE INTERVAL FOR A PROPORTION There are numerous methods available for constructing a Binomial confidence interval. The CIN is 6.67, i.e. To calculate the 95% confidence interval, we can simply plug the values into the formula. 0.67 - 1.65. The word risk is not always appropriate. Confidence Interval (CI): is the range of values that is likely to include the true population value and is used to measure the precision of the studys estimate (in this case, the precision of the Hazard Ratio). The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is To find the confidence interval around the RR itself, the two bounds of the above confidence interval can be exponentiated. A subject treated with AZT has 57% the chance of disease progression as a subject treated with placebo. 1. All Answers (7) If the incidence in non smokers was actually zero (unlikely) the relative risk would be infinity. Stack Exchange network consists of 180 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.. Visit Stack Exchange 95% confidence interval from. Bibliography: It is to be used as a guide only. Calculating confidence intervals for relative risks (odds ratios) and standardised ratios and rates Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) . 1978 Jun 24; 1 (6128):16551657. 2.7. It then combines the results using Rubin's rules and. Calculating confidence intervals for relative risks (odds ratios) and standardised ratios and rates Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) . The corresponding 95% confidence interval of [3.80, 27.27] indicates a moderate estimation uncertainty for CIN. for relative risk = exp(ln(RR) 1.96*SE(ln(RR))) to exp(ln(RR) 1.96*SE(ln(RR))) where SE(ln(RR)) = 1/A + 1/C 1/(A+B) 1/(C+D) The 95% C.I. You can take a look at the sample size calculator to learn more about this principle. For the USA: So for the USA, the lower and upper bounds of the 95% confidence interval are 34.02 and 35.98.
How do you calculate RR interval? to go by RR or PP interval. If it is 1 big box (0.2 secs) then the rate is 60/0.2 = 300 bpm. Count the number of RR intervals between two Tick marks (6 seconds) in the rhythm strip and multiply by 10 to get the bpm. This method is more effective when the rhythm is irregular. Beside this, what is the RR interval? The estimate of where the true value of a result lies is usually expressed in terms of a 95% confidence interval (CI), or confidence limits. 95% Confidence Interval for an Odds Ratio. How Prism computes the confidence interval of the relative risk CONFIDENCE INTERVAL FOR A PROPORTION There are numerous methods available for constructing a Binomial confidence interval. The CIN is 6.67, i.e. To calculate the 95% confidence interval, we can simply plug the values into the formula. 0.67 - 1.65. The word risk is not always appropriate. Confidence Interval (CI): is the range of values that is likely to include the true population value and is used to measure the precision of the studys estimate (in this case, the precision of the Hazard Ratio). The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is To find the confidence interval around the RR itself, the two bounds of the above confidence interval can be exponentiated. A subject treated with AZT has 57% the chance of disease progression as a subject treated with placebo. 1. All Answers (7) If the incidence in non smokers was actually zero (unlikely) the relative risk would be infinity. Stack Exchange network consists of 180 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.. Visit Stack Exchange 95% confidence interval from. Bibliography: It is to be used as a guide only. Calculating confidence intervals for relative risks (odds ratios) and standardised ratios and rates Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) . 1978 Jun 24; 1 (6128):16551657. 2.7. It then combines the results using Rubin's rules and. Calculating confidence intervals for relative risks (odds ratios) and standardised ratios and rates Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) . The corresponding 95% confidence interval of [3.80, 27.27] indicates a moderate estimation uncertainty for CIN. for relative risk = exp(ln(RR) 1.96*SE(ln(RR))) to exp(ln(RR) 1.96*SE(ln(RR))) where SE(ln(RR)) = 1/A + 1/C 1/(A+B) 1/(C+D) The 95% C.I. You can take a look at the sample size calculator to learn more about this principle. For the USA: So for the USA, the lower and upper bounds of the 95% confidence interval are 34.02 and 35.98.
There is no SAS program available for the Background Meta-analysis provides a useful statistical tool to effectively estimate treatment effect from multiple studies. The statistic and confidence interval as calculated above are the same as those given by the riskratio function, of epitools package for R, for the normal approximation (Wald) confidence interval: Risk ratio = 1.052 (0.670 - 1.653). Estimating risk ratios from observational data. The post Calculate Confidence Intervals in R appeared first on finnstats.
The mi estimate command first runs the estimation command on each imputation separately. The main command for running estimations on imputed data is mi estimate. Ederer F, Mantel N. Confidence limits on the ratio of two Poisson variables. Note however, how wide the 95% confidence interval for this relative risk is (due to the small numbers in column 2, as Reeza mentioned). The risk ratio is estimated as 1.43, and because the dataset is large, the 95% confidence interval is quite narrow. Statistics in Medicine, 27(17), 3301-3324. The relative risk calculator can be used to estimate the relative risk (or risk ratio) and its confidence interval for two different exposure groups. If the RR >1, and the CI does not include 1, events are significantly more likely in the treatment than the control group. Confidence Intervals Around Relative Risk To calculate the 95% confidence intervals for relative risk, we use the following formula: CI = (r1/r2) plus or minus 1.96 x square root of {(1/a x b/n1) + (1/c x d//n2)} Where r1 = a/(a+b) and r2 = c/(c+d) n1 = total number of births in group 1, those with the risk factor.
% of relative bias = [(median of adjusted relative risk estimated from 1,000 random data sets true adjusted relative risk) / true adjusted relative risk ] 100. Results for both individual studies and meta-analyses are reported with a point estimate together with an associated confidence interval.
For example, the abstract of a report of a cohort study includes the statement that In those with a [diastolic blood pressure] reading of 95-99 mm Hg the relative risk was 0.30 (P=0.034).7 What is the confidence interval around 0.30? Relative risk.
Z = 1.960. = 2.7. n = 100. Statistics in Medicine, 8(8): 987-996. Find the sample mean.
A bootstrap interval might be helpful. 1.96 SE) If the frequencies are suitably large (none less than 5), and the risk ratio not too extreme, the errors can be accepted as 'approximately' normal.
The narrower the confidence interval, the more precise the estimate. This calculator uses the following formulae to calculate the odds ratio (or) and its confidence interval (ci). Risk Reduction Calculator. b) The Attributable Risk and the corresponding 100(1-)% confidence interval. 12.4.1 Confidence intervals. 1988 May 7;296(6632):1313-6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6632.1313. In this case you should use risk difference. 1974 Sep; 100 (3):165167. hypothesis testing, such as correlation, regression slope, relative risk, and odds ratio etc. The estimate of where the true value of a result lies is usually expressed in terms of a 95% confidence interval (CI), or confidence limits. Let us now consider the case of observational data. One thousand random data sets were created, and each statistical method was applied to every data set to estimate the adjusted relative risk and its confidence interval. The approximation, however, might not be very good. To do so we simulate a new dataset, where now the treatment assignment depends on x: It is calculated as: Relative risk = [A/(A+B)] / [C/(C+D)] We can then use the following formula to calculate a confidence interval for the relative risk (RR): The multiplier of 1.96 is associated with a two-sided condence interval. It is a prefix command, like svy or by, meaning that it goes in front of whatever estimation command you're running. The 95% confidence intervals and statistical significance should accompany values for RR and OR. Edit: If you also want to report the odds ratio, you should switch the columns as well (see extended BY We can also interpret this as a 56% reduction in death, since 1-0.44=0.56. When the counts are too small for the Normal to apply, the minimum RRss is three. The relative risk can be estimated in the context of a model or using a nonmodeling approach. The risk ratio calculator will output: relative risk, two-sided confidence interval, left-sided and right-sided confidence interval, one-sided p-value and z-score, the number needed to treat to achieve the benefit for a single person (NNT Benefit) or number of people that need to be exposed for one negative outcome to occur (NNT Harm).
We would calculate the relative risk as:Relative Risk = [A/ (A+B)] / [C/ (C+D)]Relative Risk = [34/ (34+16)] / [39/ (39+11)]Relative Risk = 0.68 / 0.78Relative Risk = 0.872 The relative risk (also known as the risk ratio or prevalence ratio) is the ratio of event probabilities at two levels of a variable or two settings of the predictors in a model, where the "event" is the response level of interest. Confidence Interval. Calculate the sample average, called the bootstrap estimate. Chapter 18, Relative risk, relative and absolute risk reduction, number needed to treat and confidence intervals. Ratio of relative risk (RRR) = Test of interaction (z score) 95% confidence interval of RRR =. Elbarbary M. Understanding and expressing "Risk". A comparison of maximum likelihood and Jewell's estimators of the odds ratio and relative risk in single 2 2 tables. Think of the relative risk as being simply the ratio of proportions. Comparison of methods using a graphical approach and moving averages.
As you can see in this example, it's crucial to analyze a sample big enough to ensure that the confidence interval is sufficiently small. Randomized trial of presenting absolute v. relative risk reduction in the elicitation of patient values for heart disease prevention with conjoint analysis. J Saudi Heart Assoc. In: Better Knowledge for Better Health | Un meilleur savoir pour une meilleure sant. Relative Risk (Risk Ratio) Calculator. Relative risk online calculator This page was last edited on 6 July 2022, at 15:56 (UTC). b) The Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) and the corresponding 100(1-)% confidence interval.
The relevance of the Confidence Interval in R.R makes sense when the R.R is different from 1. [Google Scholar] Gardner MJ, Guyer PB, Barker DJ. This article has been cited by other articles in PMC. These define the range that includes the true relative risk reduction 95% of the time. Confidence intervals for the difference between. The mi estimate command first runs the estimation command on each imputation separately. Click the button Calculate to obtain; a) The Odds Ratio and the corresponding 100(1-)% confidence interval. Confidence Interval Table Confidence intervals are about risk A 99% confidence interval will be wider than a 95% confidence interval or less precise This range, with a certain level The confidence interval represents the precision with which we are able to report the effect size, and the larger the sample, the more precise the estimate There are several formulas for a binomial The confidence interval for relative risk was constructed using a method by Koopman. These define the range that includes the true relative risk reduction 95% of the time. (Precision will be affected by the studys sample size).
mi estimate. A permanent record of the analysis can be obtained by printing the page. 95% CI (RR) =. You need to know what the sample mean is before you can calculate the confidence interval. Therefore, exercisers had 0.44 times the risk of dying during the course of the study compared to non-exercisers. 95% CI (RR) =. Click the button Reset for another new calculation; Formula: Variables: (IE4) (A+C) (B+D) OUTCOME: Total "better" A+B= A = B = Total "no better" C+D : C = D= Relative risk R = 95% confidence interval = or treatment is A permanent record of the analysis can be obtained by printing the page. Sorted by: 22. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] [R] Confidence interval for relative risk Viechtbauer Wolfgang (STAT) Wolfgang.Viechtbauer at STAT.unimaas.nl Fri Nov 10 16:54:14 CET 2006. 1988 May 7;296(6632):1313-6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6632.1313. Here are the steps involved. The relative risk for a positive outcome was 0.3333 (0.12/0.36) with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.1444 to 0.7696; the z-statistic is 2.574 and the associated P-value is 0.01. Assuming the following with a confidence level of 95%: X = 22.8. It is a prefix command, like svy or by, meaning that it goes in front of whatever estimation command you're running. Walter and Cook (1991). However, the RR and OR must be interpreted in the context of the absolute risk as well as the clinical importance of the outcome in From our sample of size 10, draw a new sample, WITH replacement, of size 10.
Confidence intervals. Example: (same example, but we will compute the odds ratio instead of the risk ratio) Step 1: Find the natural log of OR. Enter the data into the table below, select the required confidence level from the dropdown menu, click "Calculate" and the results will be displayed below. This calculator was created for your own personal use and testing purposes. The confidence interval Excel function is used to calculate the confidence interval with a significance of 0.05 (i.e., a confidence level of 95%) for the mean of a sample time to commute to the office for 100 people. Previous message: [R] Confidence interval for relative risk Next message: [R] Summary, was Re: Confidence interval for relative risk Messages sorted by: The conclusion is that there is a 3-fold decreased risk in the treatment A group, and this decrease is statistically significant (P=0.01). exp (lnRR. Br Med J. 6. Full text. This calculator can be of great help in your statistical calculations and all you need to do is provide the respective inputs and tap on the calculate button to
The relative risk is 16%/28% = 0.57.
The sample mean is 30 minutes and the standard deviation is Confidence Intervals for Comparing Means of Continuous Outcomes Between Two Populations 28:24 Confidence Intervals for Binary Comparisons: Part 1, Difference in Proportions 12:07 Confidence Intervals for Binary Comparisons: Part 2, relative risk=risk of one group/risk of other group. t An exact 100(1-a)% confidence interval for the population value of OR is found by first determining a confidence interval for s
How do you find the Z score on a calculator for confidence interval?Go to the z-interval on the calculator. Press [STAT]->Calc->7.Highlight STATS. Since we have statistics for the sample already calculated, we will highlight STATS at the top.Enter Data.Calculate and interpret. Step 3: Convert the log limits back to a linear scale by exponentiating them. It then combines the results using Rubin's rules and.