Rabbit plasma 6. It involves a chain of molecular processes. ; These occur predominantly in pairs or as loose aggregates of single cells as a result of their division in irregular planes. Positive Control: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Medium-sized yellow colonies Negative Control: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Partial to Complete Inhibition. Image Source: Riraq25 (Wikipedia). Enrofloxacin is contraindicated in dogs and cats known to be hypersensitive to quinolones. It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 12 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not hemolytic on blood agar. Staphylococcus capitis is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative coccus, present as a part of the human normal flora. Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales.Under the microscope, they appear spherical (), and form in grape-like clusters. colonies of the size 1-3mm in diameter that are smooth, slightly convex, glistening, and opaque are seen on P agar. Limitations of Mannitol Salt Agar. Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms: Organisms included Staphylococcus epidermidis (six), on the hydrolysis of an active substrate by the leukocyte esterase that reacts with a diazonium salt to form a purple color. Gram-positive bacteria retain the primary stain while gram-negative bacteria take the color of the counterstain.
Staphylococcus aureus and other coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) are opportunistic pathogens associated with a large spectrum of diseases that range from skin and mucosal infections to life-threatening septicemias in humans and animals.
The method yields a semiquantitative result that is related to the total number of leukocytes that are present in the sample. Binomial name Location Acinetobacter spp: staphylococcus aureus) produce pigments that cause them to appear yellowish/golden in color when viewed under the .
When grown on a TSA plate, Staphylococcus aureus appears to be yellow to opaque in color. Anaerobios: Bacteroides spp (son resistentes muchas cepas de Bacteroides fragilis), Peptococcus spp, Peptostreptococcus spp, Streptococcus spp, Propionibacterium spp, Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp. Quaternary ammonium compounds (quats), such as benzalkonium chloride (see Fig. Some concentrated formulations have been shown to be effective low-level disinfectants. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS (S.
Staphylococcus epidermidis; Streptococcus viridans; Gastrointestinal tract.
Sterile swabs and sterile toothpicks 5.
These properties have positive effects on the skin and can help remove harmful bacteria as well as dirt and impurities. Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antimicrobial drug. For the majority of bacteria, the cell is surrounded by a cell wall. They have an approximate diameter of 2.5 to 4 mm. Quaternary ammonium compounds (quats), such as benzalkonium chloride (see Fig. Staphylococcus epidermidis, normally found on human skin, is capable of biofilm formation when it expresses polysaccharide intracellular adhesin (PIA). 1.34 for the chemical structure), are a large group of related compounds. Cerca de 2000 millones de personas han sido Phagocytosis is the process of taking in particles such as bacteria, invasive fungi, parasites, dead host cells, and cellular and foreign debris by a cell. Overnight broth cultures of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Enterococcus faecalis (on plate). It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 12 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not hemolytic on blood agar. It is a catalase-positive, coagulase-negative, facultative anaerobe that can grow by aerobic respiration or by
 0.125 Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).. [4] El principal grupo de riesgo son pacientes hospitalizados o inmunocomprometidos. Escherichia coli. Solutions of premixed ZINACEF range in color from light yellow to amber.
0.125 Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).. [4] El principal grupo de riesgo son pacientes hospitalizados o inmunocomprometidos. Escherichia coli. Solutions of premixed ZINACEF range in color from light yellow to amber. Contraindications. Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms: When the cultures are carried out, small colonies are seen, of a white or grayish color. Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales.Under the microscope, they appear spherical (), and form in grape-like clusters. Production of PIA is a virulence factor that is associated with S. epidermidis strains found in opportunistic infections. Some concentrated formulations have been shown to be effective low-level disinfectants. [23] Involucra a varios procesos moleculares. Staphylococcus aureus es un agente patognico ubicuo que es considerado como parte de la microbiota normal, se encuentra en la piel del individuo sano pero en ocasiones en que las defensas de la piel caen puede causar enfermedad. If hydrogen sulfide is produced, a black color forms in the medium.
Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).. It is recommended for the detection and enumeration of coagulase-positive Staphylococci in milk, food, and other specimens and encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefields Group B streptococci) NOTE: Most isolates of enterococci, eg, Enterococcus faecalis, and methicillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to cefepime. They have an approximate diameter of 2.5 to 4 mm. Phagocytosis occurs after the foreign body, a bacterial cell, for example, has bound to molecules called "receptors" that are on the surface of the phagocyte.
Staphylococcus epidermidis) Enterococcus faecalis Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus agalactiae. Phagocytosis is the process of taking in particles such as bacteria, invasive fungi, parasites, dead host cells, and cellular and foreign debris by a cell. La fagocitosis es el proceso de captura de partculas en el interior de una clula, ya sean bacterias, parsitos, clulas apoptticas; en definitiva, toda clase de partcula extraa. The color might change to yellow or yellow-orange after storage at 1-4C. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS (S. Staphylococcus epidermidis form thick biofilms and can cause infections associated with implanted medical devices. Binomial name Location Acinetobacter spp: It was first described by Friedrich Rosenbach in 1884. These properties have positive effects on the skin and can help remove harmful bacteria as well as dirt and impurities. This thin layer does not retain the initial crystal violet dye but picks up the pink color of the counterstain during Gram staining.
Phagocytosis is the process of taking in particles such as bacteria, invasive fungi, parasites, dead host cells, and cellular and foreign debris by a cell. 4. It is indicated for gram-positive infections and approved for the treatment of bacterial pneumonia, skin and skin structure infections, and vancomycin-resistant enterococcal (VRE) infections, including infections complicated by bacteremia.
Figure 16 shows the two different types of colonies growing on a BAP. Escherichia coli. Nitrofurantoin is not active against most strains of . It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS (S. It is a catalase-positive, coagulase-negative, facultative anaerobe that can grow by aerobic respiration or by The osmolality of the solution is approximately 300 mOsmol/kg, and the pH of thawed solutions ranges from 5 to 7.5. Limitations of Mannitol Salt Agar. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmotile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters. Figure: Gram Staining of Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Gram-positive). It contains a high concentration (about 7.510%) of salt (NaCl) which is inhibitory to most bacteria - making MSA selective against most Gram-negative and selective for some 3% Hydrogen peroxide solution Procedure: (work in pairs) 1. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. Staphylococcus aureus is highly vulnerable to destruction by heat treatment and nearly all sanitizing agents.
El agar sangre es una combinacin de un agar base (agar nutritivo) con el agregado de 5 % de sangre ovina, [1] tambin puede usarse sangre humana, para cultivos en una placa de Agar.El agar sangre aporta muchos factores de enriquecimiento.Se usa tambin para ver la capacidad hemoltica de los microorganismos patgenos (que es un factor de Virulencia). [24] Se produce cuando estos elementos se unen a receptores de la superficie del fagocito, cambiando su estructura tridimensional e induciendo Staphylococcus epidermidis form thick biofilms and can cause infections associated with implanted medical devices. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a gram-positive bacterium that is part of the usual bacterial flora on the body surface.
Production of PIA is a virulence factor that is associated with S. epidermidis strains found in opportunistic infections. Staphylococcus capitis is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative coccus, present as a part of the human normal flora.
Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). Staphylococcus epidermidis, or another Staphylococcus species.
This section needs expansion. 3 About 15 percent colonies of the size 1-3mm in diameter that are smooth, slightly convex, glistening, and opaque are seen on P agar. Figure: Gram Staining of Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Gram-positive).
5. It is indicated for gram-positive infections and approved for the treatment of bacterial pneumonia, skin and skin structure infections, and vancomycin-resistant enterococcal (VRE) infections, including infections complicated by bacteremia.
S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals.
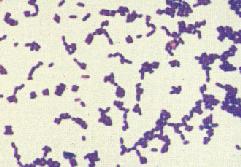
The color might change to yellow or yellow-orange after storage at 1-4C. This section needs expansion. Thus, the presence of this bacterium or its enterotoxins in Susceptibility Testing. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a gram positive bacterium that when looked at under a microscope it appears to be a cluster of what looks like purple circles.
Contraindications. If hydrogen sulfide is produced, a black color forms in the medium.
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein.It is a form of venous access.Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. [24] Se produce cuando estos elementos se unen a receptores de la superficie del fagocito, cambiando su estructura tridimensional e induciendo Staphylococcus epidermidis. It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. Positive Control: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Medium-sized yellow colonies Negative Control: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Partial to Complete Inhibition. It contains a high concentration (about 7.510%) of salt (NaCl) which is inhibitory to most bacteria - making MSA selective against most Gram-negative and selective for some Organisms included Staphylococcus epidermidis (six), on the hydrolysis of an active substrate by the leukocyte esterase that reacts with a diazonium salt to form a purple color. Cell Wall. 1.34 for the chemical structure), are a large group of related compounds. It involves a chain of molecular processes.
Cerca de 2000 millones de personas han sido
The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist
El agar sangre es una combinacin de un agar base (agar nutritivo) con el agregado de 5 % de sangre ovina, [1] tambin puede usarse sangre humana, para cultivos en una placa de Agar.El agar sangre aporta muchos factores de enriquecimiento.Se usa tambin para ver la capacidad hemoltica de los microorganismos patgenos (que es un factor de Virulencia). staphylococcus aureus) produce pigments that cause them to appear yellowish/golden in color when viewed under the .
Citrobacter amalonaticus Citrobacter diversus Citrobacter freundii Klebsiella oxytoca Klebsiella ozaenae. It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas.
Enrofloxacin is contraindicated in dogs and cats known to be hypersensitive to quinolones.
[4] El principal grupo de riesgo son pacientes hospitalizados o inmunocomprometidos.
Staphylococcus epidermidis Bacillus spp.
Quality Control on Mannitol Salt Agar. Cerca de 2000 millones de personas han sido
The organism pictured on the far left is positive for hydrogen sulfide production. It is recommended for the detection and enumeration of coagulase-positive Staphylococci in milk, food, and other specimens and encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while Susceptibility Testing.
Overnight broth cultures of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Enterococcus faecalis (on plate). When the cultures are carried out, small colonies are seen, of a white or grayish color. Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefields Group B streptococci) NOTE: Most isolates of enterococci, eg, Enterococcus faecalis, and methicillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to cefepime.
The epidermis is composed of the outermost layers of the skin.
[23] Involucra a varios procesos moleculares.
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used as a selective and differential medium for the isolation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from clinical and non-clinical specimens. It was first described by Friedrich Rosenbach in 1884. Staphylococcus capitis is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative coccus, present as a part of the human normal flora.
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) is used as a selective and differential medium for the isolation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from clinical and non-clinical specimens.
It contains a high concentration (about 7.510%) of salt (NaCl) which is inhibitory to most bacteria - making MSA selective against most Gram-negative and selective for some
Escherichia coli. They produce several extracellular proteins contributing
Abstract. It involves a chain of molecular processes. Thus, the presence of this bacterium or its enterotoxins in
Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).. Staphylococcus epidermidis; Staphylococcus saprophyticus; * Some of the species (e.g. staphylococcus aureus) produce pigments that cause them to appear yellowish/golden in color when viewed under the . Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology.It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. Grampositivos: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Micrococcus spp. For the majority of bacteria, the cell is surrounded by a cell wall. Sterile swabs and sterile toothpicks 5.
3 About 15 percent Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefields Group B streptococci) NOTE: Most isolates of enterococci, eg, Enterococcus faecalis, and methicillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to cefepime. [24] Se produce cuando estos elementos se unen a receptores de la superficie del fagocito, cambiando su estructura tridimensional e induciendo The epidermis is composed of the outermost layers of the skin. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a gram positive bacterium that when looked at under a microscope it appears to be a cluster of what looks like purple circles.
The epidermis is composed of the outermost layers of the skin.
When the cultures are carried out, small colonies are seen, of a white or grayish color. This shape is known as cocci. The solution is intended for intravenous (IV) use after thawing to room temperature. Several Staphylococcus species other than aureus are mannitol positive and produce yellow colonies surrounded by yellow zones on It is recommended for the detection and enumeration of coagulase-positive Staphylococci in milk, food, and other specimens and encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while If hydrogen sulfide is produced, a black color forms in the medium. Group D streptococci Viridans group streptococci . 3% Hydrogen peroxide solution Procedure: (work in pairs) 1. A Gram stain can also serve to assess the quality of a clinical specimen. Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms: 0.125 Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Quality Control on Mannitol Salt Agar. Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS).
The osmolality of the solution is approximately 300 mOsmol/kg, and the pH of thawed solutions ranges from 5 to 7.5. Staphylococcus spp.
The solution is intended for intravenous (IV) use after thawing to room temperature. Some concentrated formulations have been shown to be effective low-level disinfectants. Staphylococcus epidermidis es una especie de bacteria de la familia Staphylococcaceae [2] que forma parte de la microbiota normal de la piel y las mucosas humanas junto con otras especies de estafilococos coagulasa-negativos. Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections Eugenio Pontieri, in Pet-To-Man Travelling Staphylococci, 2018.
[23] Involucra a varios procesos moleculares. These properties have positive effects on the skin and can help remove harmful bacteria as well as dirt and impurities. Staphylococcus aureus is highly vulnerable to destruction by heat treatment and nearly all sanitizing agents. Enrofloxacin is contraindicated in dogs and cats known to be hypersensitive to quinolones. . Sterile swabs and sterile toothpicks 5. Staphylococcus epidermidis es una especie de bacteria de la familia Staphylococcaceae [2] que forma parte de la microbiota normal de la piel y las mucosas humanas junto con otras especies de estafilococos coagulasa-negativos. Proteus mirabilis is positive for H 2 S production. Staphylococcus epidermidis. Staphylococcus epidermidis; Staphylococcus saprophyticus; * Some of the species (e.g. Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology.It encourages the growth of a group of certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. Grampositivos: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Micrococcus spp. Gram-Negative Aerobes. Figure: Gram Staining of Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Gram-positive). Staphylococcus aureus and other coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) are opportunistic pathogens associated with a large spectrum of diseases that range from skin and mucosal infections to life-threatening septicemias in humans and animals.