Common central anticholinergic adverse effects include headache, impaired memory, reduced cognitive function, behavioral disturbances, anxiety, and insomnia at What this tells us is that anticholinergics, especially for treating GI motility, have a lot of side effects. Key elements in the toxidrome are: Dilated pupils. Other common examples include meclizine, scopolamine and ipratropium. These thankfully subsided, but having been off of the medication for almost two years, my memory is still terrible, and I am only 25. Side effects. The adverse effects of cholinergic stimulants include mostly rash and digestive system complaints, including queasiness, loose stools, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, muscle pain , increased salivation, increase in stomach acid production, and diarrhea. As this score is not based on effects on cognition or CNS-specific effects, it is a preferred tool for measuring the peripheral anticholinergic effects of medications, whereas the ACB is better suited for measuring central effects of medications (Boustani et al., 2008). Anticholinergic drugs are used to treat a variety of conditions: Dizziness (including vertigo and motion sickness -related symptoms) Extrapyramidal symptoms, a potential side-effect of Scopolamine is found in the shrub Hyoscyamus niger and Scopolia carniolica. Amplification of the tachycardic effect of sympathomimetic drugs. Individuals should be advised that psychomotor and cognitive impairment may be present even in the absence of subjective symptoms. Side effects of anticholinergics. Total Anticholinergic Load: Possible side effects of anticholinergic medications include: Anticholinergics relax the bronchial smooth musculature, which Its important to know that, unless necessary, the use of anticholinergics should be These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. CVS effects of anticholinergics. Tricyclic and tricyclic-related antidepressantsantimuscarinic effectstooth decay and oral healthdecreased alertnesssuicidal feelingsserotonin syndromeSIADH (Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion)diabetesneuroleptic malignant syndromehypomania or mania Prescribe anticholinergic drugs with caution in older or frail people or people with complex multi-morbidities. Atropine consists of equal parts of d-and 1-hyoscyamine, but the anitimuscarinic activity is almost wholly due to the 1-isomer. Anticholinergics. Anticholinergic drugs are considered selectively antimuscarinic.
Some of these side effects are more pronounced in certain populations, such as older adults. 
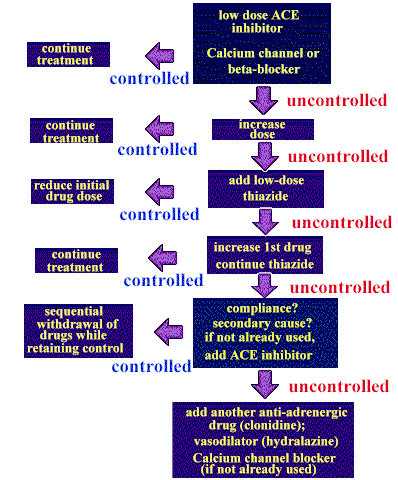 Anticholinergics are used in hyperhidrosis treatment when other less invasive options have not adequately improved quality of life. Other side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, disorientation, agitation, blurry vision, dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.
Anticholinergics are used in hyperhidrosis treatment when other less invasive options have not adequately improved quality of life. Other side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, disorientation, agitation, blurry vision, dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.  What are anticholinergic effects. Over the past Anticholinergics, such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl, are a class of medications that have been used to treat several different conditions including antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) that are most often associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs), such as haloperidol and fluphenazine. Perhaps the mechanism underlying the potential effects of anticholinergic drugs is not solely through blocking acetylcholine and causing an excess of Alzheimer disease, so future research should give consideration to possible mechanisms. These include: Dry mouth due to the inhibition of the salivary glands Sore throat due to decreased mucus production Absence of sweating Increased body temperature Light Most commonly, anticholinergics can cause the following side effects: drowsiness or sedation blurred vision dizziness urinary retention confusion or delirium hallucinations Oral anticholinergics reduce sweat production throughout the body. The NIA-supported findings appeared online Jan. 26, 2015, in JAMA Internal Medicine. In fact, even small increases in so-called anticholinergic burden or load increases the risk of morbidity & mortality in older individuals. Even when used as instructed, anticholinergics can have some unpleasant side effects. Even if we wanted to simply decrease stomach acid, it would also cause dry mouth dizzinessextreme drowsinessfeversevere hallucinationsconfusiontrouble breathingclumsiness and slurred speechfast heartbeatflushing and warmth of the skin The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: 3. Anticholinergic drugs block the effects of acetylcholine (Ach), a neurotransmitter in the brain that stimulates muscle contractions and plays a role in learning, memory, and attention. The anticholinergic effects that can impair driving performance include blurred vision, sedation, confusion, ataxia, tremulousness, and myoclonic jerking. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or In essence, they also lyse and block the effects of parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) so they are also called as parasympatholytics. 1. relax smooth muscles in the respiratory and GI - asthma treatment -spasmolytic agents. The potential dangers of the concomitant administration of 2 or more drugs with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties have been known for a long time. core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.
What are anticholinergic effects. Over the past Anticholinergics, such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl, are a class of medications that have been used to treat several different conditions including antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) that are most often associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs), such as haloperidol and fluphenazine. Perhaps the mechanism underlying the potential effects of anticholinergic drugs is not solely through blocking acetylcholine and causing an excess of Alzheimer disease, so future research should give consideration to possible mechanisms. These include: Dry mouth due to the inhibition of the salivary glands Sore throat due to decreased mucus production Absence of sweating Increased body temperature Light Most commonly, anticholinergics can cause the following side effects: drowsiness or sedation blurred vision dizziness urinary retention confusion or delirium hallucinations Oral anticholinergics reduce sweat production throughout the body. The NIA-supported findings appeared online Jan. 26, 2015, in JAMA Internal Medicine. In fact, even small increases in so-called anticholinergic burden or load increases the risk of morbidity & mortality in older individuals. Even when used as instructed, anticholinergics can have some unpleasant side effects. Even if we wanted to simply decrease stomach acid, it would also cause dry mouth dizzinessextreme drowsinessfeversevere hallucinationsconfusiontrouble breathingclumsiness and slurred speechfast heartbeatflushing and warmth of the skin The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: 3. Anticholinergic drugs block the effects of acetylcholine (Ach), a neurotransmitter in the brain that stimulates muscle contractions and plays a role in learning, memory, and attention. The anticholinergic effects that can impair driving performance include blurred vision, sedation, confusion, ataxia, tremulousness, and myoclonic jerking. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or In essence, they also lyse and block the effects of parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) so they are also called as parasympatholytics. 1. relax smooth muscles in the respiratory and GI - asthma treatment -spasmolytic agents. The potential dangers of the concomitant administration of 2 or more drugs with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties have been known for a long time. core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.
The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: dry mouth; blurry vision ; constipation; Seniors have the greatest risk of side effects from these drugs. No one has done the research to determine if reducing the anticholinergic burden will reverse memory problems. metoprolol.
A. Anticholinergics are a class of drugs that work specifically to antagonize acetylcholine (Ach) at muscarinic receptors in the parasympathetic nervous system. 3.3 Neurological disease and anticholinergic medications Delirium. Individuals should be Naturally, Mixing anticholinergics with alcohol have similar side effects as overdosing with anticholinergics, which include dizziness, fever, confusion, accelerated heart rate, trouble breathing, hallucinations, unconsciousness and even death. Older adults who take anticholinergic drugs, which are commonly prescribed for a wide range of health conditions, may be at significantly higher risk of developing dementiaand the greater the use of the drugs, the higher the potential risk. The anticholinergic drugs for OAB are able to enter the central nervous system and lead to central side effects. Anticholinergic agents decrease the acid production in the stomach that slows down the natural gut movements, thus relaxing the muscles in several organs such as the An anticholinergic drug is prescribed for the patient. Anticholinergic exposure for as short as 2 weeks has shown to be associated with a decline in global cognitive function, visual memory, verbal fluency, and on activities of daily living.. -. They are also called antispasmodics. Here are seven common types of anticholinergic medication that older adults should avoid, or use with caution: 1. They found that people diagnosed with dementia were up to 30% more likely to have been prescribed anticholinergic medications for Parkinson's, bladder problems, or depression. Other medications with less severe anticholinergic effects include: Alprazolam (Xanax) Cetirizine (Zyrtec) Codeine; Furosemide (Lasix) Loperamide (Imodium) Loratadine (Alavert, Claritin) Ranitidine (Zantac) Tizanidine (Zanaflex) A full list of anticholinergic drugs can be found here. EZmed explains anticholinergic toxicity syndrome including signs and symptoms, causes, medication drug effects, diagnosis, treatment, physostigmine antidote, and Sources and Chemistry of Anticholinergic Drugs: Atropine is obtained from Atropa belladonna, and Datura stramonium. [The adverse effects of anticholinergic drugs] Abstract Acetylcholine is one of the main neurotransmitters.
1 Older/frail patients are more likely to experience adverse effects with anticholinergics such as constipation, urinary retention, dry mouth/eyes, sedation, confusion, delirium, photophobia, falls and reduced cognition. Background: Anticholinergic drugs in elderly people have been associated with some serious side-effects. Tachycardia. Constipation. By blocking the action of acetylcholine, anticholinergics As a person ages they are more susceptible to the adverse effects of medications for a variety of reasons including decreased renal and hepatic function, the presence of
Anticholinergic drugs act directly on the nerves in the sweat glands to show a perspiration suppression effect (1) start at a low dose of 15 mg once to twice a day, increasing as tolerated to 30 mg tds. treat asthma.
Table of Common Drugs Handbook covers dosage, side effects, interactions, uses. The most common side effects of anticholinergics are dry mouth and constipation. Symptoms of an anticholinergic overdose include: Other common terms for these drugs are anti-muscarinics, vagolytics, and parasympatholytics. Confusion. When possible, the use of anticholinergics should be avoided in the Dry mouth and eyes. The most common side effects of anticholinergics are dry mouth and constipation. Anticholinergic Drugs Anticholinergics can be helpful for tremor and may ease dystonia associated with wearing-off or peak-dose effect. Sedating antihistamines. A large British study has found that the frequent use of a common class of medications known as anticholinergics may be associated with an increased risk of dementia among older people. Published online Monday by JAMA Internal Medicine, it confirms previous research on the medications risk. Increased anticholinergic effect with antiparkinson drugs, antihistamines, antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants. Anticholinergics are drugs that oppose the effects of acetylcholine. The Takeaway. Some of the Summary. 4. Other less common side effects include heartburn, blurry vision, rapid heartbeat, flushed skin and trouble urinating. An extended-release form taken once a day might cause fewer side effects. Objectives To estimate the association between the duration and level of exposure to different classes of anticholinergic drugs and subsequent incident dementia. 9. Taking anticholinergic drugs at high doses or for a long time may significantly increase your risk for developing Alzheimer's disease and other dementias, say researchers azithromycin. Increased anticholinergic effect with antiparkinson drugs, antihistamines, antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants. Hence, this review aimed to focus on the mechanisms of CNS and CVS side effects of anticholinergic drugs used in OAB treatment, whic " Abstract - Cited by 2 (0 self) - Add to MetaCart. Participants 40 770 patients aged 65-99 with a diagnosis of dementia between April Decreased urine production. Anticholinergics are a broad group of medicines that act on the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. Anticholinergics can also have side effects that can vary in severity. This drug was introduced in the 1980s and reestablished anticholinergics as a therapy for bronchospastic disorders. There is increasing evidence that a high anticholinergic load is linked to the development of cognitive impairment and even dementia. Insomnia. Side effects can vary depending on the specific drug you are taking. Includes App for iPhone, iPad, and Android smartphone + tablet. RATIONALE: Histamine release and stimulation of histamine receptor(s) is one of the primary events in the allergic response and inhibition of histamine receptor activity has been successful Due to the fact that anticholinergic drugs dont produce euphoric or pleasurable effects, they are considered to have a low potential for abuse; hence the reason many are over-the-counter. Common offenders: scopolamine patch for
"(Anticholinergic drugs) can cause a range of side effects such as constipation, difficulty with bladder control," she said. Tachycardia. There are numerous side effects associated with their use including dry mouth and urinary retention.
The bodys production of acetylcholine diminishes with age, so blocking its effects can deliver a double whammy to older people.
25 Comments. The pharmacologic effects of anticholinergics used in anesthesia are summarized in Table 8-2. Anticholinergics are used for maintenance therapy of bronchoconstriction associated with asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. The anticholinergic effects that can impair driving performance include blurred vision, sedation, confusion, ataxia, tremulousness, and myoclonic jerking. Listed below are examples of some anticholinergic side effects: Dry mouth Difficulty in swallowing Constipation Paralytic ileus Nausea or vomiting Increased heart rate Urinary retention Difficulty Caution is therefore warranted when taking cholinergic drugs. This may be because of several factors, including age, clinical conditions, medicines used, and laboratory-derived causes. Generally speaking, these compounds 1 These dangers are pharmacodynamic drug interactions resulting from additive anticholinergic effectsalthough occasionally there may be a pharmacokinetic mechanism acting simultaneously. As such, you can have severe side effects from these anticholinergic drugs. Key elements in the toxidrome are: Dilated pupils. Anticholinergic medications have many different side effects. Anticholinergic drugs have long played an important role in the management of bladder symptoms, which reduce incontinence and urgency 1 while improving quality of life. Ipratropium is a muscarinic antagonist, what is its indication. These agents present a risk that is especially The prime example is diphenhydramine (brand name Benadryl), which is available over-the-counter and has strong anticholinergic activity. What are the possible side effects of anticholinergics? These four elements suggest an anticholinergic toxidrome. Effects of Anticholinergics on smooth msucles. The potential dangers of the concomitant administration of 2 or more drugs with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties have been known for a long time. Constipation. To view the entire name and generic drugs. The drugs implicated are commonly used, estimated to be taken by about 20% of the older adult population for many conditions. Aside from depression, these drugs historically have been prescribed for a variety of conditions, such as: Some studies have found an increased risk of mortality.
For dry mouth, try In essence, they also lyse and block the effects of parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) so they are Explore these free sample topics: hydroxychloroquine. heroin) laced with anticholinergics, which increases likelihood of toxicity. Delirium. Drug Interactions of Anticholinergics. Side effects may vary depending on the medical These medications work on the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). A. Anticholinergic drugs work by blocking the effects of acetylcholine, a substance that transmits messages in the nervous system. They have little effect on other symptoms of The cellular effects of acetylcholine, which are mediated through second messengers, are inhibited. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Anticholinergics accidentally or deliberately instilled in eyes, but they cause more widely dilated pupils that will not constrict to bright light. September 29, 2020.
Side effects can appear at any time, even many years after starting a medication. Anticholinergic agents consumed at appropriate doses hardly provide any side effects. How to reverse the effects of anticholinergic drugs? Anticholinergic drugs block muscarinic receptor activation and inhibit the spontaneous detrusor contractions found in overactive bladder. Dry skin This is an essential element, which helps The increased risks from anticholinergic drugs were shown to be cumulative, based on the number of anticholinergic drugs taken and the strength of each drugs anticholinergic effect. It is involved in autonomic activities of the peripheral organs and forms a Delirium. Patients in Turkey tend to attend primary care centers to have prescriptions of the Decreased sweat production. The effects of anticholinergics on cognition varies substantially depending on the study.
Anxiety. An extended-release form taken once a day might cause fewer side effects. Adverse/Side Effects Anticholinergics should be used Another anticholinergic agent, ipratropium (Atrovent), is used primarily in pulmonary care. The term anticholinergics refers to medications, drugs, or other compounds that block the activity of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Drug Interactions of Anticholinergics. Difficulty urinating. The man has a comorbidity of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
In the brain, acetylcholine is involved in Anticholinergics. Memory impairment. Anticholinergics, Respiratory: Dosing, Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Patient Handouts, Pricing and more from Medscape Reference Your risk of side effects is higher if: you are taking higher doses; you take the medication for a long time; you are taking more than one anticholinergic medication.
Setting General practices in the UK contributing to the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. The probable side effects depend on the medical history of the person, dosage, and specific type of anticholinergics taken. Side effects of respiratory anticholinergics may include the following: Headache Nasopharyngitis (inflammation of nose and throat) Upper respiratory tract infection COPD Possible side effects include: hyperthermia lack of sweating rapid or irregular heartbeat flushing urinary retention blurred vision glaucoma vision loss dilated pupils Effects of anticholinergic drugs at nicotinic cholinergic receptors is little / nil as compared at muscarinic receptors. Anticholinergics mitigate For dry mouth, try sucking hard candy or chewing gum to produce more saliva. vagal blockade if taken in large doses which leads to tachycardia. Amplification of the tachycardic effect Neuroscientists have been warning for years that a class of medications called anticholinergic ( AC or aCH) drugs are bad for your Possible side effects of anticholinergic medications include: Sometimes, therapeutic effects in one organ system may have undesirable side effects in other organ systems. Side effects of anticholinergics. Dry skin This is an essential element, which helps separate anticholinergic toxidromes from sympathomimetic toxidromes. That said, some people take illicit drugs (e.g. This can cause unwanted side effects. Anticholinergic and Cholinergic Drugs are commonly used in medicine and prescribed for many conditions. In addition, a biological method, the SAA assay produces different and contradictory results in different studies. Anticholinergic Drugs - Increased Fall Risk There is a growing epidemic in the senior community of adverse effects to anticholinergic drugs. Headaches. Adverse effects of anticholinergic medications Side effects of anticholinergics include: Dry mouth Blurred vision Dry eyes Constipation Urinary retention Dizziness due to drop in blood pressure - Dementias, including neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia. The anticholinergic risk is higher in dementias with cholinergic deficit such as Alzheimers disease, Lewy body dementia and Parkinsons dementia. - Schizophrenia. - Acute hallucinatory episode. - Depression. - Anxiety. - Parkinsons disease. - Cardiovascular diseases. More items Possible side effects of anticholinergic medications include: Dry mouth due to inhibition of the salivary gland Atropine is currently the only widely used anticholinergic drug.
Some side effects that are usually more noticeable in older adults include issues with memory, confusion, and hallucinations. 1 These dangers
However, these benefits need to be considered in relation to potential adverse effects. Anticholinergic drugs are commonly used in veterinary anesthesia to treat and/or prevent anesthetic and preanesthetic bradycardia, decrease airway and salivary secretions, dilate the pupil, block vagally mediated reflexes (viscerovagal, oculocardiac, Branham), and block the effects of parasympathomimetic drugs. A new study provides the strongest evidence that anticholinergic drugs may increase the risk for dementia in older adults. Side effects can include: dry mouth blurry vision constipation drowsiness sedation hallucinations memory problems trouble urinating confusion delirium decreased sweating The Adverse Effects of Anticholinergic Drugs: CNS stimulation Tachycardia Constipation Dry mouth Urinary retention Decreased sweating (hot & dry skin) Blurred vision We included a large representative sample of people diagnosed with dementia and matched controls. Inhaled anticholinergics are medications used to dilate and decongest the bronchial passages in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ().Anticholinergics block the activity of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that nerve endings secrete to make muscles contract.. Acetylcholine works by binding to protein molecules known as muscarinic receptors A) Atropine (generic) B) Dicyclomine (generic) C) Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) D) Methscopolamine (Pamine) C. A 73-year-old male with Parkinson's disease comes to the clinic for routine care. anticholinergics is a topic covered in the Davis's Drug Guide. The most common side effects of anticholinergics include blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, difficulty emptying the bladder, impaired sweating, and rapid heart rate. risk of adverse effects. - posted in Brain Health: I was placed on a dose of 250mg amitriptyline for a year, before going down to 100mg due to adverse muscular side effects. Design Case-control study. A recently published study focussed on the impact of anticholinergic drugs in the cardiopathic elderly patients and enrolled 3761 people (average age 83 years, average follow-up 1.4 suggesting that coronary diseases could provide a favorable substrate for the manifestation of the arrhythmogenic effects of anticholinergics. Its not surprising that problems with short-term Anticholinergics are drugs that oppose the effects of acetylcholine. Anticholinergic drugs act on the muscarinic receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems and inhibit acetylcholine-mediated responses by

 Anticholinergics are used in hyperhidrosis treatment when other less invasive options have not adequately improved quality of life. Other side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, disorientation, agitation, blurry vision, dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.
Anticholinergics are used in hyperhidrosis treatment when other less invasive options have not adequately improved quality of life. Other side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, disorientation, agitation, blurry vision, dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.  What are anticholinergic effects. Over the past Anticholinergics, such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl, are a class of medications that have been used to treat several different conditions including antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) that are most often associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs), such as haloperidol and fluphenazine. Perhaps the mechanism underlying the potential effects of anticholinergic drugs is not solely through blocking acetylcholine and causing an excess of Alzheimer disease, so future research should give consideration to possible mechanisms. These include: Dry mouth due to the inhibition of the salivary glands Sore throat due to decreased mucus production Absence of sweating Increased body temperature Light Most commonly, anticholinergics can cause the following side effects: drowsiness or sedation blurred vision dizziness urinary retention confusion or delirium hallucinations Oral anticholinergics reduce sweat production throughout the body. The NIA-supported findings appeared online Jan. 26, 2015, in JAMA Internal Medicine. In fact, even small increases in so-called anticholinergic burden or load increases the risk of morbidity & mortality in older individuals. Even when used as instructed, anticholinergics can have some unpleasant side effects. Even if we wanted to simply decrease stomach acid, it would also cause dry mouth dizzinessextreme drowsinessfeversevere hallucinationsconfusiontrouble breathingclumsiness and slurred speechfast heartbeatflushing and warmth of the skin The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: 3. Anticholinergic drugs block the effects of acetylcholine (Ach), a neurotransmitter in the brain that stimulates muscle contractions and plays a role in learning, memory, and attention. The anticholinergic effects that can impair driving performance include blurred vision, sedation, confusion, ataxia, tremulousness, and myoclonic jerking. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or In essence, they also lyse and block the effects of parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) so they are also called as parasympatholytics. 1. relax smooth muscles in the respiratory and GI - asthma treatment -spasmolytic agents. The potential dangers of the concomitant administration of 2 or more drugs with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties have been known for a long time. core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.
What are anticholinergic effects. Over the past Anticholinergics, such as benztropine and trihexyphenidyl, are a class of medications that have been used to treat several different conditions including antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) that are most often associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs), such as haloperidol and fluphenazine. Perhaps the mechanism underlying the potential effects of anticholinergic drugs is not solely through blocking acetylcholine and causing an excess of Alzheimer disease, so future research should give consideration to possible mechanisms. These include: Dry mouth due to the inhibition of the salivary glands Sore throat due to decreased mucus production Absence of sweating Increased body temperature Light Most commonly, anticholinergics can cause the following side effects: drowsiness or sedation blurred vision dizziness urinary retention confusion or delirium hallucinations Oral anticholinergics reduce sweat production throughout the body. The NIA-supported findings appeared online Jan. 26, 2015, in JAMA Internal Medicine. In fact, even small increases in so-called anticholinergic burden or load increases the risk of morbidity & mortality in older individuals. Even when used as instructed, anticholinergics can have some unpleasant side effects. Even if we wanted to simply decrease stomach acid, it would also cause dry mouth dizzinessextreme drowsinessfeversevere hallucinationsconfusiontrouble breathingclumsiness and slurred speechfast heartbeatflushing and warmth of the skin The most common side effects of anticholinergic drugs include: 3. Anticholinergic drugs block the effects of acetylcholine (Ach), a neurotransmitter in the brain that stimulates muscle contractions and plays a role in learning, memory, and attention. The anticholinergic effects that can impair driving performance include blurred vision, sedation, confusion, ataxia, tremulousness, and myoclonic jerking. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or In essence, they also lyse and block the effects of parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) so they are also called as parasympatholytics. 1. relax smooth muscles in the respiratory and GI - asthma treatment -spasmolytic agents. The potential dangers of the concomitant administration of 2 or more drugs with anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) properties have been known for a long time. core elements of the anticholinergic toxidrome.